
Reducing the risk of clot formation in blood samples.
Inadequate mixing of a sample can lead to a blood sample clotting
Clot formation in blood gas samples can be a result of errors in the preanalytical phase of arterial blood gas analysis.
If the anticoagulant in a blood gas syringe isn’t completely dissolved in the blood sample, blood clots may form in the sample. When your blood sample is clotted, then consider it unsuitable for analysis. [1]
Outcomes of clotted blood samples
Clots in the blood gas sample can lead to:
Blood clots can block the pathway of the blood gas analyzer, leading to analyzer downtime. If clots are introduced into the blood gas analyzer, you’ll find the results biased or the analyzer inoperable. [1]
Reduce the risk of clots in blood samples
Inadequate mixing increases the risk of clot formation in the sample. Mixing your blood sample adequately after collection reduces the risk of blood clots.
When the sample is free of air bubbles, mix the anticoagulant and blood sample adequately. The heparin in the sample needs to dissolve in the blood to reduce clot formation. The recommended technique suggests rolling the syringe between your palms. Then gently and repeatedly invert it vertically. [1-2]
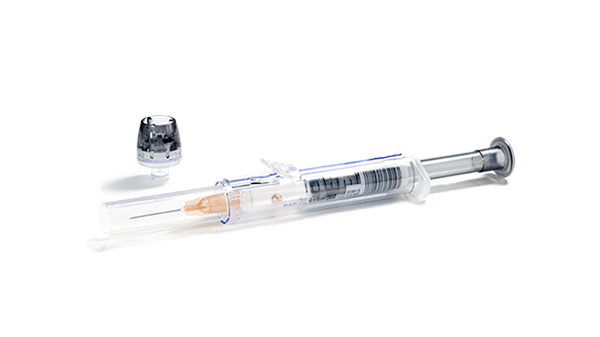
At Radiometer, we designed the safePICO blood gas syringe to help you adequately mix your sample. Dry electrolyte balanced heparin in our safePICO syringes in combination with automatic mixing helps to reduce the risk of your blood sample clotting.
After sample collection, the built-in mixing ball in the syringe helps you produce a homogeneous sample.The safePICO syringe is designed to reduce the risk of other preanalytical errors. In addition to a clotted blood sample, safePICO can help to remove air bubbles safely from the sample and to reduce the risk of hemolysis due to mixing, needlestick injuries or patient-sample mix-up.

References
2. CLSI. Blood Gas and pH Analysis and Related Measurements; Approved Guideline—Second Edition. CLSI document C46-A2 [ISBN 1-56238-694-8). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Road, Suite 2500, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087 USA, 2009.
Cookies are used on this website
Use of cookiesPlease enter a valid email
We will be sending an e-mail invitation to you shortly to sign in using Microsoft Azure AD.
It seems that your e-mail is not registered with us
Please click "Get started" in the e-mail to complete the registration process
Radiometer is using Microsoft AZURE Active Directory to authenticate users
Radiometer uses Azure AD to provide our customers and partners secure access to documents, resources, and other services on our customer portal.
If your organization is already using Azure AD you can use the same credentials to access Radiometer's customer portal.
Key benefits
- Allow the use of existing Active Directory credentials
- Single-sign on experience
- Use same credentials to access future services
Request access
You will receive an invitation to access our services via e-mail when your request has been approved.
When you accept the invitation, and your organization is already using AZURE AD, you can use the same credentials to access Radiometer's customer portal. Otherwise, a one-time password will be sent via e-mail to sign in.

